|
BIOMASS:
Biomass has been a major energy source, prior to the
discovery of fossil fuels like coal and petroleum. Even
though its role is presently diminished in developed
countries, it is still widely used in rural communities of
the developing countries for their energy needs in terms
of cooking and limited industrial use.
Biomass is a natural substance available, which stores
solar energy by the process of photosynthesis in the
presence of sunlight. It chiefly contains cellulose,
hemicellulose and lignin, with an average composition of C6H10O5,
with slight variations depending on the nature of the
biomass.
Biomass has always been an important energy source for the
country considering the benefits it offers. It is
renewable, widely available, carbon-neutral and has the
potential to provide significant employment in the rural
areas. Biomass is also capable of providing firm energy.
About 32% of the total primary energy use in the country
is still derived from biomass and more than 70% of the
country’s population depends upon it for its energy
needs.
The Government of Madhya Pradesh has taken note of the
growing recognition of impacts of climate change and
recognizes the need to tackle challenges that arise on
account of these impacts through integrated policy
prescriptions and programmes aimed at mitigation of
impacts and adaptation to reduce vulnerability of systems.
Based on this green initiative, by endorsing the essential
need to prevent avoidable erosion of natural carbon –
energy resources the state is endowed with, the state is
committed to promote promotion of generation of
electricity from Renewable Energy sources.
Potential:
The ‘Biomass Resource Atlas of India” projects the gross
potential for energy generation from Agricultural sources
at 1386.2 MWe and 2060.6 MWe from forests ,wastelands
respectively in the state of Madhya Pradesh.
The biomass wise potential in the state has been given
below:
|
Biomass |
Power Potential
(kWe) |
|
Husk |
248.161 |
|
Stalks |
886.57 |
|
Leaves |
561.467 |
|
Cobs |
41.08 |
|
Shell |
158.11 |
|
Bark |
477.15 |
|
Residue |
0.3 |
|
Branches |
477.15 |
|
Others |
0.06 |
|
Twigs |
477.15 |
|
Straw |
44 |
|
Pod |
75.3 |
Achievement:
Biomass based power projects with a cumulative capacity of
around 32 MW has been commissioned in the state as on 19
November,2010.
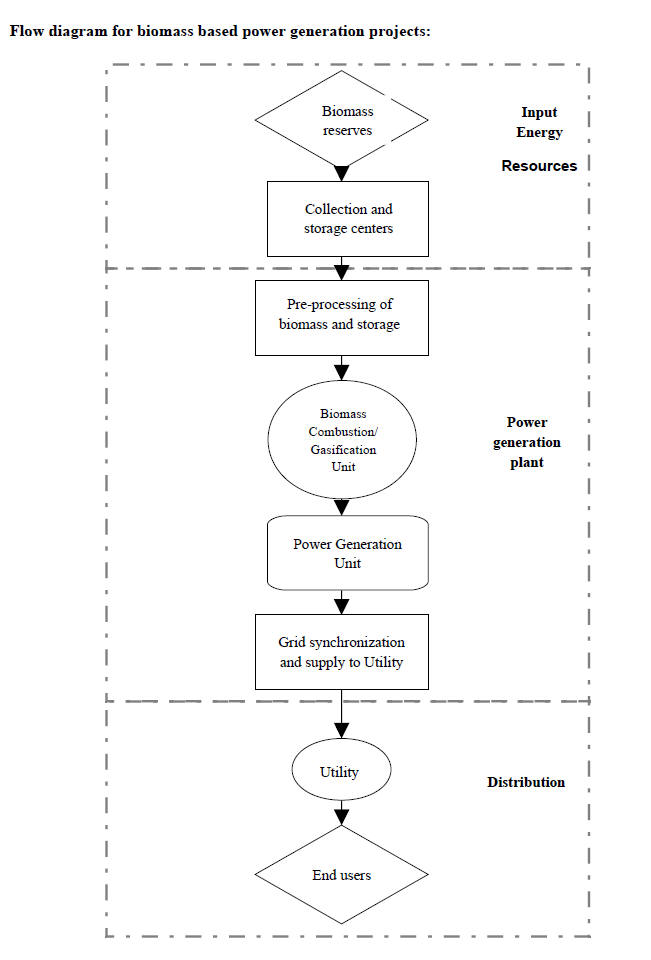
Technology:
1.
Bagasse based Co-generation :
In
simple terms, cogeneration is the process of using a
single fuel to produce more than one form of energy in
sequence. Cogeneration of steam and electricity can
significantly increase the overall efficiencies of fuel
utilization in process industries. A minimum condition for
cogeneration is the simultaneous requirement of heat and
electricity in a favourable ratio, which is well fulfilled
in the sugar industry. The thermodynamics of electricity
production necessitates the rejection of a large quantity
of heat to a lower temperature sink. In normal electricity
generation plants, this heat rejection takes place in
condensers where up to 70% of heat in steam is rejected to
the atmosphere. In cogeneration mode, however, this heat
is not wasted and is instead used to meet process heating
requirement. The overall efficiency of fuel utilization
can thus be increased to 60% or even higher in some cases.
Capacity of cogeneration projects can range from a few
kilowatts to several megawatts of electricity generation
along with simultaneous production of heat ranging from
less than a hundred kWth (kilowatts thermal) to many MWth
(megawatts thermal).
2.
Biomass based Power Generation :
The technology for generation of electricity from these
biomass materials is similar to the conventional
coal-based thermal power generation. The biomass is burnt
in boilers to generate steam, which drives a turbo
alternator for generation of electricity.
3.
Biomass Gasification :
Biomass gasification is thermo-chemical conversion of
solid biomass into a combustible gas mixture (producer
gas) through a partial combustion route with air supply
restricted to less than that theoretically required for
full combustion. Typical composition of producer gas is
Carbon Monoxide (18%-20%), Hydrogen (15%-20%), Methane
(1%-5%), Carbon dioxide (9%-12%), Nitrogen (45%-55%). The
calorific value of the producer gas is in the range of
1000-1200 kcal/m3.
|